On-chain perpetual exchanges closed 2026 at cumulative trading volume surpassing $12 trillion, up from $4 trillion at the beginning of the year. As per data from DeFilama, around 65% of lifetime perpetual DEX trading volume, approximately $7.9 trillion, was generated in a year. This ends the debate around whether decentralized derivatives were experimental. Traders voted with capital.
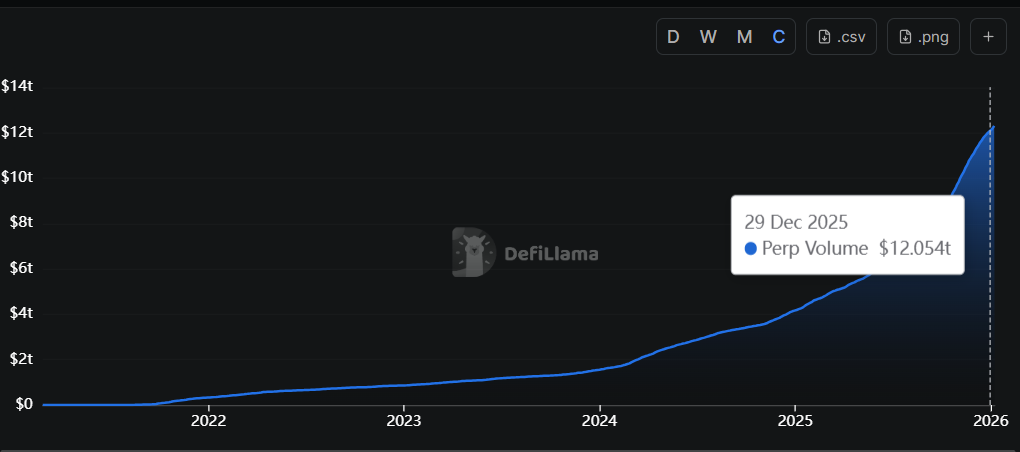
Source: https://defillama.com/perps
The momentum was also evident from the record-breaking DEX-to-CEX derivatives trading volumes ratio that reached 11.7% by the end of the year. Users increasingly chose verifiable execution, self-custody, and transparent liquidation logic over opaque centralized futures books.
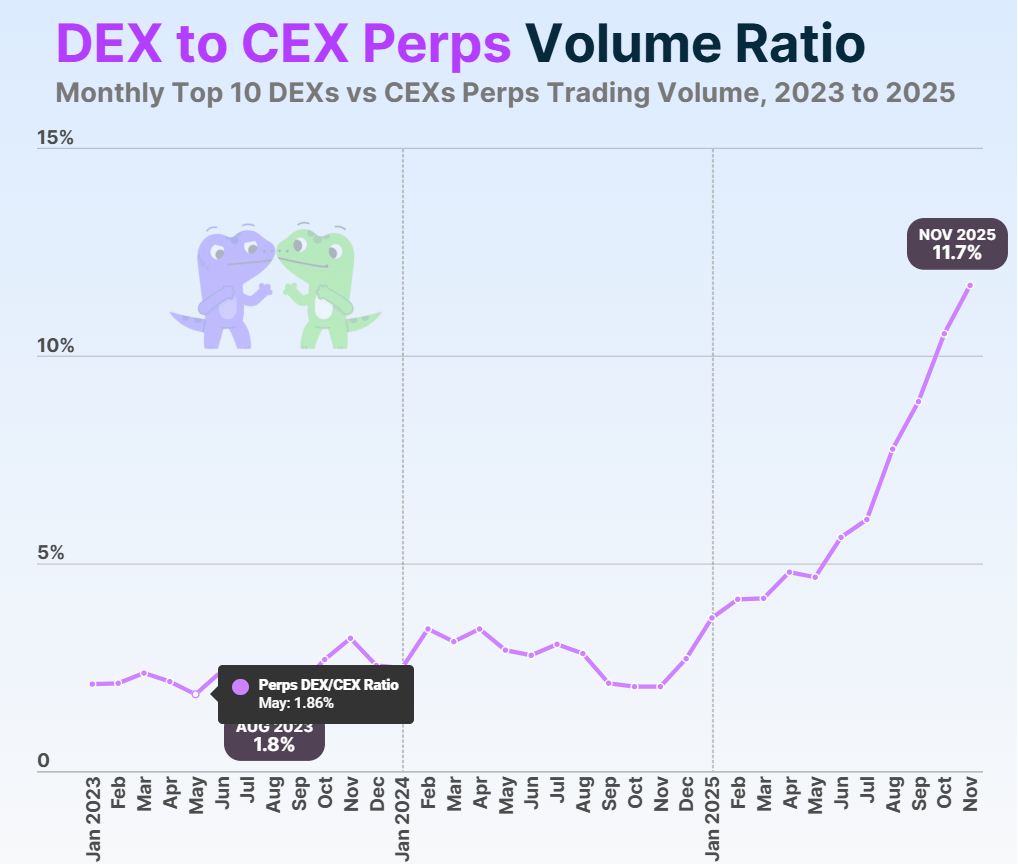
Source: https://www.coingecko.com/research/publications/dex-to-cex-ratio
Monthly on-chain perp volumes peaked at $1.2 trillion, while ecosystems like Solana alone crossed $451 billion in annual perp trading. It was a huge year for perpetual futures decentralized exchanges.
Hypeliquid, Aster, and Solana Platforms like Lighter have proven that orderbook-style, fully on-chain perpetual trading can scale, without compromising speed, capital efficiency, or trader control.
Let’s break down what actually needs to be built to launch a decentralized perpetual futures crypto exchange like Lighter.
What Makes Lighter Different From Typical Perpetual Futures DEXs?
Most early decentralized crypto futures exchanges leaned heavily on AMMs or hybrid custody models. Lighter took a harder route, and that’s precisely why it attracted serious traders.
Lighter Vs Aster Vs Hyperliquid: A Quick Differentiation
| Dimension | Lighter | Aster | Hyperliquid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Design Philosophy | Fully on-chain, verifiable infrastructure | Performance-first hybrid model | Capital-efficient AMM-first design |
| Execution Model | On-chain orderbook with ZK-verified matching | Off-chain matching, on-chain settlement | AMM-based execution |
| Custody Model | Fully non-custodial, no shadow state | Partial off-chain state | Non-custodial but AMM-governed |
| Transparency Level | Maximum (all trades provable) | Medium (execution not fully verifiable) | Medium (pricing logic transparent, matching implicit) |
| Capital Efficiency | High (20–30% better than AMMs) | Moderate | High for AMM perps |
| Latency Optimization | ZK + batching | Centralized matcher speed | Optimized curve-based pricing |
| Liquidation Logic | Verifiable, deterministic | Engine-driven, less transparent | AMM-based, curve-driven |
| Engineering Complexity | Very high (hardest route) | Medium | Medium |
| Best Suited For | Pro traders, infra-first protocols | UX-focused growth platforms | Liquidity-driven trading at scale |
Lighter Perpetual DEX’s Key differentiators:
- Fully on-chain execution: Traders are matched and settled on-chain. No hidden off-chain engine holding user state. Every position, fill, and liquidation is verifiable on the chain.
- Orderbook-based trading: Traders place limit and market orders, not swaps against the pool. The predictable fills and tighter spreads are the features that professionals expect.
- Higher capital efficiency: Margin is used more precisely than AMM-based perpetual futures crypto exchanges, so less capital sits idle. A survey reveals that these ZK-verified matching and optimized margin accounting have delivered 20-30% better capital usage than AMM perps.
- No shadow custody: The protocol never temporarily controls user funds, reducing system risk.
In 2025, Lighter even overtook the incumbents – Hyperliquid and Aster, with a 24h peak volume reaching $9.41 billion. The architecture achieved a 12-15% share of total perpetual DEX open interest in mid November 2025.
What is the Core Architecture of a Lighter-Style On-Chain Perpetual DEX?
A. Execution Layer (How Your Trade Happens)
This crypto futures trading layer answers one basic trader’s question.
“When I click Buy or Sell, what decides my price?”
- In some DEXs, trades are decided off-chain by a private system.
- In others (like Lighter), trades are decided on the blockchain itself.
Why this matters:
- On-chain execution means no hidden rules.
- Anyone can verify why a trade was filled at a certain price.
- It’s slower to build, but harder to manipulate.
In simple terms:
In the case of fully on-chain perpetual futures contracts trading, the match or trade isn’t decided by a black box. It follows visible, fixed rules that are not easy to manipulate.
B. Margin & Position Engine (How Your Profit or Loss Is Tracked)
This crypto perpetual futures exchange part answers this question for traders:
“How much am I winning or losing right now?”
- Most traders use cross-margin, where all their positions share one balance. In simple words, their money works as one shared safety net for all trades.
- Traders’ profit or loss is updated continuously using live market prices.
- Every trade follows a strict flow: open → adjust → close → settle.
- The system constantly checks how much money traders actually have at a point in time, updates PnL, and uses the updated balance to decide whether the trade can stay open or must be closed.
Why this matters:
- If the system checks traders’ losses too late or gets them wrong, it can close their trade even when they still have enough money. And that’s a real financial loss, not just a display problem.
C. Liquidation & Risk Engine (What Happens When a Trade Goes Wrong)
This answers the scary question for those trading perpetual futures.
“What if the market moves against me?”
- If losses reach a danger zone (usually 80-90% of your margin), action kicks in.
- Instead of killing the whole position, many decentralized exchange software now partially close it.
- A shared insurance pool absorbs extreme losses.
Why this matters:
- Full liquidations cause panic and market crashes, whereas partial liquidations keep markets stable and fair.
D. Price Oracles (Where Prices Come From)
This answers the following question for those trading perpetual futures contracts.
“Who decides what the ‘real price of crypto perpetual futures’ is?”
- DEXs don’t guess prices. They pull them from trusted external sources.
- Two prices are used:
- Index price: What the broader market says
- Mark price: What is your PnL and liquidation use
- Speed is critical in price tracking. Even a 1-2 second delay can break everything.
Platforms use oracle providers like Pyth, Chainlink, plus averaging methods, to avoid price manipulation.
Bad prices = bad liquidations = no trust.
| Component | Purpose | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Layer | Matching & settlement | Prevents unfair fills |
| Margin Engine | PnL & leverage control | Avoids false liquidations |
| Liquidation Engine | Risk containment | Stops cascade failures |
| Oracles | Price integrity | Protects against manipulation |
What Makes Traders Stay on Crypto Futures Exchange Like Lighter?
For a trader finding the best perpetual futures DEX, these three things matter the most:
- Can I enter and exit trades without price shocks?
- Will my money be safe during volatility?
- Does this feel usable when markets move fast?
If a trader is not satisfied with any of these answers, he leaves.
- Liquidity
Liquidity simply means how much trading activity a crypto futures exchange platform can handle without prices jumping wildly. It’s not optional as it is the only decisive factor for HNW, institutional investors, or retail traders who are going to make big trades.
- If liquidity is low, even small trades move prices.
- That causes slippage, which silently eats trader profits.
In 2025, data showed that platforms with less than $100M in depth suffered 25-30% more slippage during volatile markets.
That’s why leading perpetual DEXs in 2025:
- Kept a base layer of protocol-owned liquidity.
- Rewarded liquidity providers (10-15% APY) from trading fees, not short-term token emissions.
- Tie incentives to real volume, not temporary yield farming.
On-chain perpetual DEX platforms like Lighter maintained $2-4B in daily depth, allowing large trades to execute without sudden price swings.
- Smart Contracts & Security Fundamentals
Unlike spot DEX, decentralized crypto futures trading is risky by nature, so the system must be built and trained to behave accurately under stress.
Those trading perpetual futures ensure the following:
- The rules for liquidations must be fixed and predictable.
- Price data must be reliable.
- Critical risk logic should not change unexpectedly.
This is why a serious on-chain crypto futures exchange must:
- Keep the core logic unchangeable.
- Limit upgrades to non-critical parts like UI or incentives.
- Focus audits on liquidation paths, oracle handling, and reentrancy.
- UX Realities
That’s where the most perpetual futures DEXs fail. The most common failure points in perpetual DEX development include:
- Too many wallet steps cause friction that kills retention.
- Interfaces that slow traders down are a big red flag.
- High gas fees when markets are volatile.
Gas spikes due to volatility push traders away. The January 2026 liquidation cascade caused 300% short-term gas spike.
In 2025, a clear winner was decentralized crypto futures exchange development tactics that enabled the following:
- Fewer clicks to trade.
- Gasless or abstracted transactions.
- Mobile-first layouts
Decentralized perpetual futures trading exchanges that implemented account abstraction, gasless flows, and mobile-first interfaces boosted retention by more than 25%.
Build Vs Buy: What is the Fastest Path to Launch a Perpetual Futures Crypto Exchange?
| Factor | Build From Scratch | White Label Crypto Exchange With Perpetual Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Time to Launch | 18–24 months | 6–9 months |
| Engineering Effort | Very high (custom everything) | Moderate (core modules pre-built) |
| Cost Range | $5–10 million | ~40% lower than full build |
| Risk Level | High (new bugs, new logic) | Lower (battle-tested components) |
| Oracle Integration | Built manually | Pre-integrated |
| Risk & Liquidation Engine | Designed from zero | Already implemented |
| Audit Time | Longer, repeated audits | Faster audits |
| Best For | Teams building long-term core infrastructure | Teams focused on speed and market entry |
White label crypto exchange with perpetual futures trading stack accelerates UI design, oracle integration, risk engines, and liquidity bootstrapping.
Final Word
With $12+ trillion in cumulative volume, on-chain perpetual DEXs are no longer a fringe experiment. Platforms like Lighter demonstrated that scalability, transparency, and capital efficiency can coexist.
The next generation of winners won’t chase hype cycles, but they’ll build a decentralized perpetual futures exchange the way serious financial markets are built.
Deterministic, Resilient, and Boringly Reliable.
At Antier, that is exactly how we approach on-chain perpetual futures trading exchange development. From execution engines and margin systems to liquidation logic, oracle integration, and liquidity design, we help teams build infrastructure that can withstand real market stress, not just demo-day traffic.
Whether you’re building from the ground up or accelerating with a modular or white label crypto exchange with perpetual futures trading stack, Antier delivers platforms designed to perform reliably under real market stress.
The volume has already arrived. The standards are rising.
Now it’s about execution, and Antier is built for that.
Frequently Asked Questions
01. What was the cumulative trading volume of on-chain perpetual exchanges in 2026?
The cumulative trading volume of on-chain perpetual exchanges in 2026 surpassed $12 trillion, up from $4 trillion at the beginning of the year.
02. How much of the lifetime perpetual DEX trading volume was generated in 2026?
Approximately 65% of the lifetime perpetual DEX trading volume, or about $7.9 trillion, was generated in 2026.
03. What distinguishes Lighter from typical perpetual futures DEXs?
Lighter is fully on-chain with verifiable infrastructure, whereas typical perpetual futures DEXs often rely on AMMs or hybrid custody models, making Lighter more appealing to serious traders.