Supply chains worldwide face unprecedented challenges. According to the World Economic Forum, a staggering $2.1 trillion is lost annually due to inefficiencies in how products move from manufacturers to consumers. These losses stem from fraud, delays, documentation errors, and a critical lack of end-to-end visibility.
RWA Tokenization in Supply Chain—creating secure digital representations of physical assets—offers a promising solution to these persistent issues. This guide explores the role of tokenization in Supply chain management, benefits, and use cases.
Understanding Tokenization in Supply Chain Management
Tokenization means turning real or digital items into digital tokens stored on a blockchain. In supply chains, this helps represent goods or documents in a digital form.
For example, a batch of medicine can be turned into a digital token. That token includes key details like where it came from, how it was handled, and when it expires. As the batch moves through the supply chain, the token follows it, recording every step without the chance of changes or tampering. Smart contracts can also be used to automate deals as items move along.
This helps prevent theft, ensures taxes and tariffs are tracked, and makes the whole process more secure and efficient.

How is Tokenization Used in Supply Chains?
Tokenization helps make the supply chain more transparent and reliable by creating one clear version of the truth. Some common uses include:
- Invoice tokenization – Turning invoices into digital tokens makes it easier to get financing, fight fraud, and speed up payments. It’s especially helpful for smaller suppliers deep in the supply chain.
- Inventory tokenization – Making inventory digital helps businesses see what they have in real time and avoid having too much or too little stock.
- Product tokenization – Industries like seafood use this to track products closely, making it easier to trace their origin and journey.
Benefits Of Supply Chain Tokenization
1. Addresses the Transparency Crisis
Supply chain fraud has become increasingly sophisticated. Traditional systems rely heavily on trust between parties with limited visibility beyond their immediate partners. RWA Tokenization in the Supply chain transforms this dynamic by creating an immutable digital ledger where every product maintains a verifiable digital identity throughout its journey.
2. Eliminate Costly Manual Processes
Many organizations still depend on paper-based documentation, which can lead to delayed shipments due to missing paperwork, extended payment cycles, lengthy dispute resolution processes, and administrative overheads.
Supply chain tokenization fixes these problems through smart contracts—self-executing agreements with terms written into code. Tokenized supply chains can automate payments, compliance verification, and penalty assessments. Organizations implementing these solutions report reducing processing times by up to 80%.
3. Fix Liquidity Challenges for SMEs
Small and medium-sized businesses often face cash flow challenges while waiting for payments. RWA tokenization in inventory and shipments enables them to be used as collateral for financing or traded instantly in decentralized marketplaces, transforming illiquid assets into working capital.
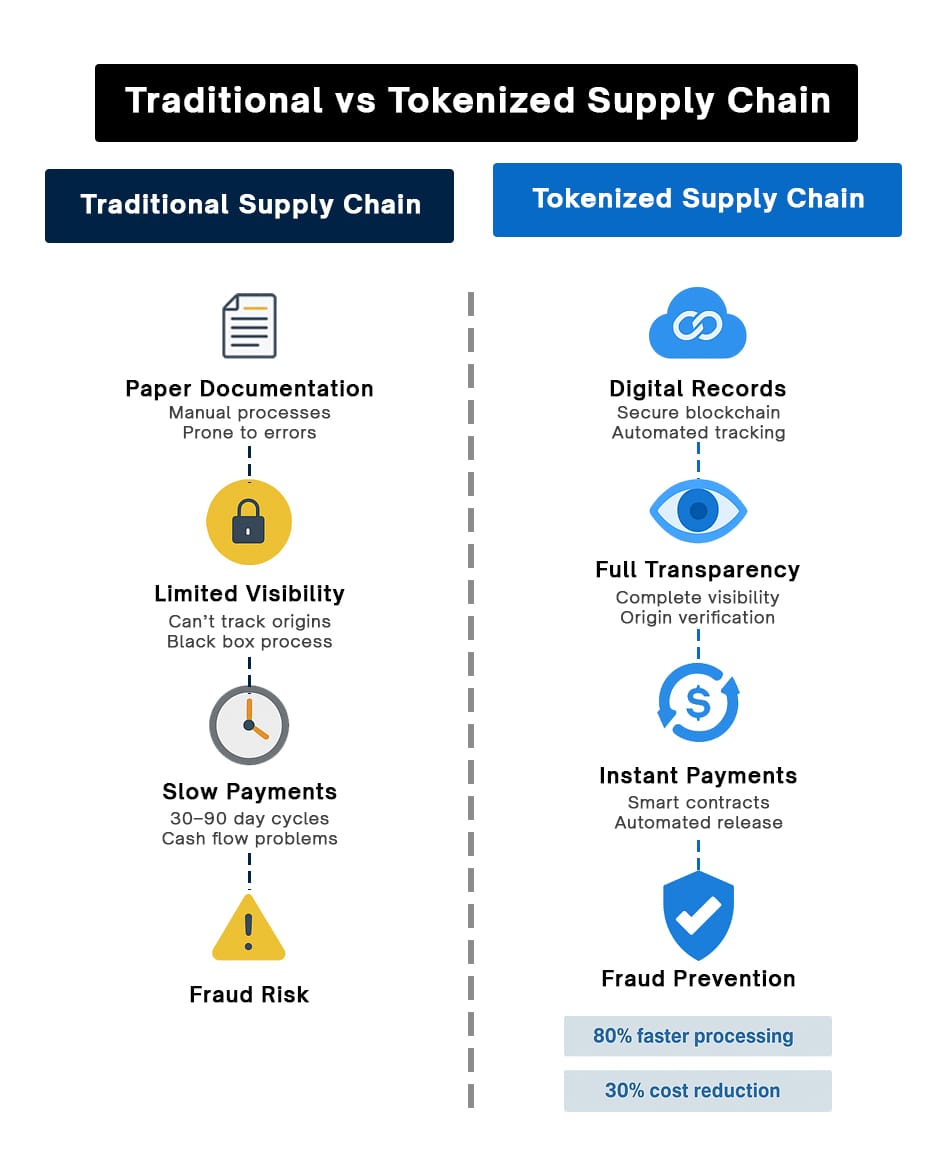
How RWA Tokenization Works for Supply Chain and Inventory?
1. Digitizing Physical Assets
Tokenization creates a digital token that represents a physical product. Each token contains:
- A unique identifier linked to physical tracking mechanisms (RFID tags, QR codes)
- Comprehensive historical data, including manufacturer information and quality inspection results
- Secure ownership records that transfer via blockchain when possession changes hands
For example, Luxury brands can tokenize individual high-value products, allowing customers to scan QR codes to verify authenticity and review the product’s journey, effectively combating counterfeiting.
2. Smart Contracts Creation
Smart contracts serve as the operational backbone of tokenized supply chains, which enable:
- Automatic release of payments when goods arrive and pass quality checks.
- Calculation of penalties for delayed shipments based on real-time tracking data.
- Verification of compliance with handling requirements.
- Triggering insurance claims when damage occurs during transit.
For example, with RWA Tokenization, Food exporters can now implement smart contracts that release payment only after IoT sensors confirm products have maintained appropriate temperatures throughout shipping.
3. Enhance Operations Through AI
Artificial intelligence amplifies tokenization benefits through:
- AI algorithms anticipate inventory needs before shortages occur
- Machine learning identifies patterns indicating fraudulent activities
- AI-powered systems minimize fuel consumption and transit time
- Algorithms predict product deterioration based on environmental conditions
Essential Features for a Tokenization Platform
A comprehensive Supply chain tokenization platform should support:
Multi-Chain Compatibility
- Enterprise blockchain solutions for organizations requiring private networks
- Public blockchain networks enabling broader market participation
- Hybrid architectures maintain sensitive information privately while utilizing public networks for verification
IoT Integration and Real-Time Tracking
Connecting physical assets to digital tokens requires:
- RFID and NFC tags enable automatic scanning in warehouses
- GPS tracking provides continuous location updates
- Environmental sensors monitor conditions such as temperature and humidity
These technologies ensure that token data accurately reflects real-world conditions, allowing pharmaceutical companies to prove that temperature-sensitive medications remained within safe ranges throughout transit.
Compliance and Legal Framework
- Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) verification for all participants.
- Automated tax calculation for cross-border transactions
- Detailed audit trails satisfying regulatory reporting requirements
- Industry-specific compliance capabilities
User-Friendly Interfaces
A well-designed platform includes customized interfaces for various participants:
- Supplier Dashboards: Tools for uploading certifications and tracking payments
- Buyer Portals: Interfaces for verifying product origins and managing purchases
- Logistics Control Centers: Views for optimizing routes and documenting deliveries
Revenue Models for Tokenization Solutions
Subscription-Based Services
Successful platforms implement tiered subscription models:
- Basic Tier ($99-199/month): Core tracking and simple smart contracts
- Professional Tier ($500-999/month): Advanced analytics and moderate AI integration
- Enterprise Tier (Custom pricing): Comprehensive capabilities and tailored implementations
Transaction Fee Structures
Platforms can generate revenue through:
- Percentage-based fees (0.1% to 1%) on tokenized trades
- Micro-fees for specific actions, such as token transfers
- Volume-based pricing with reduced rates for high-transaction customers
White-Label Technology Licensing
Many companies prefer offering supply chain solutions under their brands through:
- Branded implementations with customized features
- Revenue-sharing arrangements with partners
- Integration packages for existing enterprise systems

Overcoming Implementation Challenges
1. Addressing Adoption Resistance
Implementation strategies include:
- Starting with high-risk, high-value industries where fraud prevention delivers immediate ROI
- Implementing pilot programs with clearly defined metrics
- Developing phased adoption plans to minimize operational disruption
2. Solving Technical Scalability Limitations
Forward-thinking solutions include:
- Implementing Layer 2 blockchain protocols to reduce costs and increase throughput
- Utilizing sharding to distribute processing loads efficiently
- Developing hybrid architectures optimizing for security and performance
3. Navigating Regulatory Uncertainty
Organizations can mitigate regulatory risks by:
- Partnering with specialized legal-tech compliance providers
- Engaging proactively with regulators
- Building flexible systems adaptable to changing requirements
Future Directions in Tokenized Supply Chains
1. Integration with Decentralized Finance
The convergence with DeFi creates powerful possibilities:
- Businesses obtaining immediate financing using tokenized inventory as collateral
- Suppliers accessing competitive financing through transparent risk assessment
- Smart contracts directing payments to multiple parties based on predefined agreements
2. Metaverse Commerce Applications
As digital and physical worlds merge:
- Virtual warehouses will display digital representations linked to physical inventory
- Customers will interact with product tokens to access provenance information
- Digital twins will simulate scenarios to optimize real-world operations
3. Autonomous Supply Chain Operations
Advanced Supply chain tokenization combines with AI to create self-managing supply networks:
- Inventory systems autonomously maintain optimal stock levels
- Self-executing procurement processes triggered by real-time demand signals
- Dynamic pricing models adjusting based on supply chain conditions
4. Implementation Roadmap
Organizations interested in supply chain tokenization should follow this approach:
- Identify a Specific Use Case: Select a focused application area rather than attempting an enterprise-wide implementation initially
- Select Appropriate Technologies: Evaluate blockchain platforms, IoT devices, and AI capabilities based on specific requirements.
- Establish Strategic Partnerships: Collaborate with technology providers and industry peers.
- Conduct Controlled Pilots: Test the solution in limited environments before broader deployment
- Gather and Apply Feedback: Continuously refine based on user experiences.
- Scale Strategically: Expand to additional product lines or regions based on demonstrated value

Take Away
The tokenization of supply chains represents more than incremental improvement—it offers a fundamental reimagining of global commerce. Analysts project that the blockchain supply chain market will reach $9.85 billion by 2025. Organizations adopting tokenization today position themselves advantageously and will thrive in tomorrow’s transparent commerce ecosystem.
Ready to Build Your Tokenized Supply Chain Platform?
Antier brings years of expertise in building secure, scalable tokenization platforms tailored to supply chain needs. From smart contract development to IoT sensor integration and regulatory compliance, the team ensures your solution is enterprise-ready, fraud-proof, and future-proof. Whether you’re a startup or an established logistics firm, partnering with Antier means faster deployment, lower risks, and a Tokenized Supply Chain platform that businesses will trust. Let’s transform supply chains together—reach out today and take the first step toward a transparent, automated future.








