For years, AI systems were reactive – answering questions or executing instructions once and stopping. Modern businesses, however, demand more: systems that think, plan, and act autonomously. AI agents fulfill this need, functioning as smart collaborators that can research competitors, resolve customer issues, coordinate operations, and carry out complex, multi-step workflows.
Understanding how AI agents work, the types of AI agents, and their practical use cases is critical for modern enterprises. Companies now seek robust AI agent platforms that integrate intelligence, memory, tools, and orchestration at scale.
Did You Know?
|
This guide provides a step-by-step blueprint to build an AI agent platform, insights into AI agent frameworks, and tips on partnering with top AI agent companies to drive real-world impact.
Understanding AI Agent Platforms
Before diving into architecture or implementation, it’s important to clearly understand what an AI agent platform actually is and how it differs from chatbots, assistants, or standalone AI tools.
An AI agent is an autonomous software entity capable of understanding goals, reasoning through multiple steps, interacting with tools or environments, and adjusting its actions based on outcomes. In simple terms, this answers the foundational question: what is AI agent technology designed to do? It doesn’t just respond – it acts with intent.
However, when organizations deploy more than one agent, connect them to real systems, and allow them to operate across workflows, they quickly outgrow single-agent setups. This is where an AI agent platform comes in.
An AI agent platform is an integrated system that enables the creation, orchestration, monitoring, and governance of multiple AI agents operating together. It provides shared infrastructure for reasoning, memory, tools, security, and lifecycle management – transforming individual agents into a scalable intelligence layer for the organization.
Build Smarter AI Agents for Your Business Today!
Real-World AI Agent Platform Use Cases
An AI agent platform enables a wide range of applications, including:
- Autonomous research and reporting systems
- Customer support agents with action capabilities
- Internal workflow automation agents
- Sales, CRM, and operations intelligence
- Compliance, policy, and document intelligence
How AI Agents Work: Inside the Agent’s Brain
To truly understand the power of AI agents, you need to look beyond interfaces and outputs and examine how AI agents work internally. Unlike traditional software or conversational AI, an agent operates through a continuous decision-making loop – one that closely mirrors human problem-solving behavior.
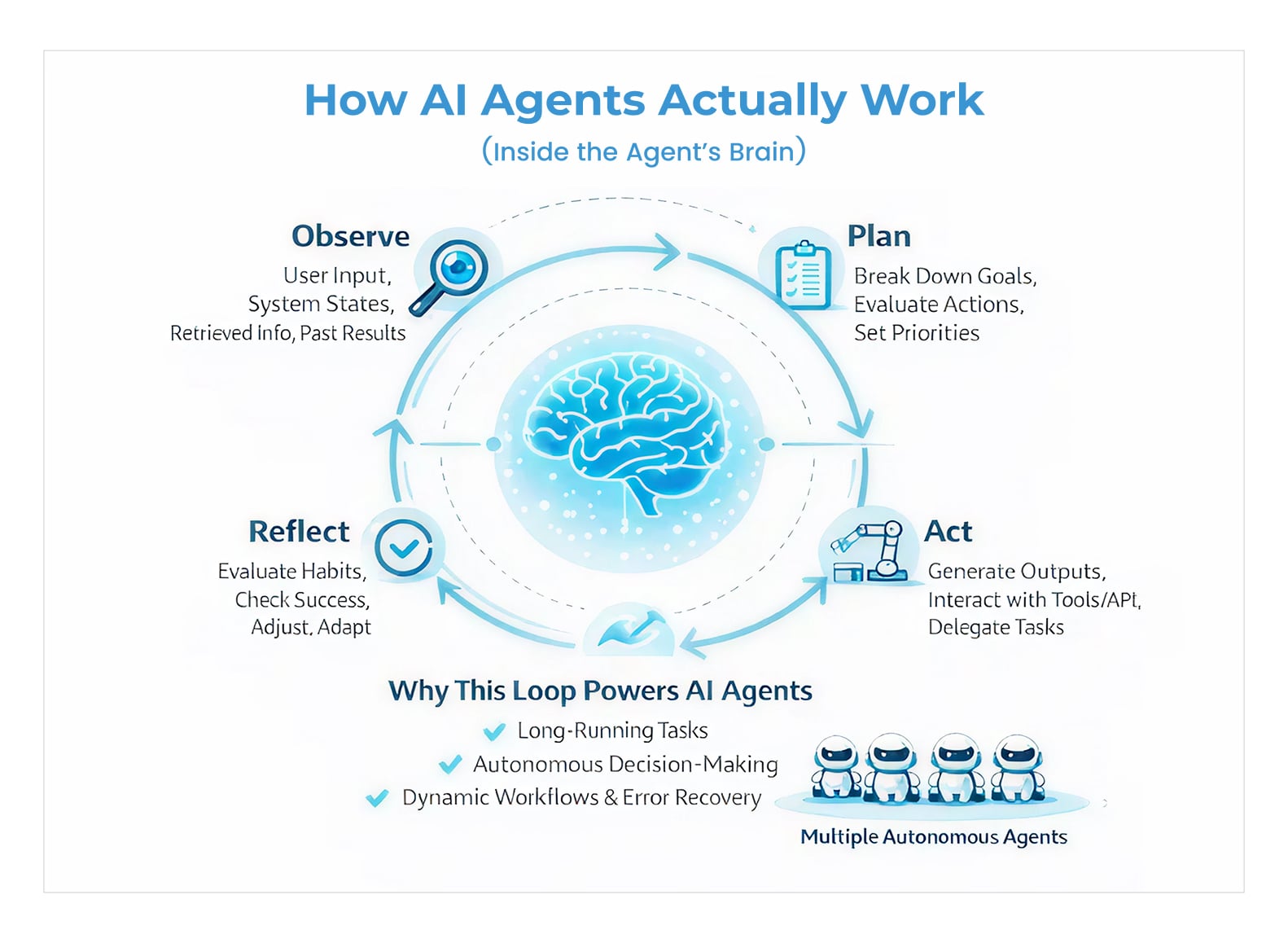
At the core of every AI agent is a simple but powerful cycle: observe, plan, act, and reflect.
The Agent Decision Loop Explained
1. Observe
The agent begins by interpreting inputs from its environment. This may include:
- User instructions
- System states
- Retrieved information
- Results from previous actions
This observation phase gives the agent situational awareness – context that shapes its next move.
2. Plan
Instead of immediately responding, the agent decides what needs to be done. This is where reasoning happens.
The agent:
- Breaks a goal into smaller steps
- Evaluates possible actions
- Prioritizes tasks based on constraints
This planning phase is a defining trait of autonomous intelligence and a major reason types of AI agents can vary so widely from simple task agents to complex multi-step problem solvers.
3. Act
Once a plan is chosen, the agent executes actions. Actions may include:
- Generating structured outputs
- Calling tools or APIs
- Requesting additional information
- Delegating subtasks to other agents
This step turns reasoning into real-world impact and is why AI agents are fundamentally different from passive AI assistants.
4. Reflect
After acting, the agent evaluates the result:
- Did the action succeed?
- Is more information needed?
- Should the plan be adjusted?
Reflection enables adaptation – a key capability that separates agents from static automation scripts.
Why This Loop Changes Everything
This internal loop explains what AI agent behavior is at a fundamental level. Instead of producing a single response, the agent continuously refines its actions until the goal is achieved or constraints are met.
This model enables:
- Long-running tasks
- Dynamic workflows
- Error recovery
- Autonomous decision-making
Many modern AI agent frameworks are built specifically to support this loop, allowing developers to structure reasoning, actions, and feedback without hardcoding every step.
Core Components of an AI Agent Platform (High-Level Only)
Once you understand how AI agents work, the next question naturally becomes: what does it take to run them reliably in real-world systems? This is where an AI agent platform comes into play.
An AI agent platform is not a single technology. It’s a coordinated system of components that allows agents to think, act, learn, and operate safely at scale. Each component exists to solve a specific problem, and removing any one of them creates instability or failure.
Below are the core components every production-ready AI agent platform must include.
1. Agent Control & Lifecycle Management
This component governs the agent’s existence from start to finish.
It is responsible for:
- Initiating agent tasks
- Managing execution loops
- Handling retries and failures
- Ending or pausing agents when goals are met
Without lifecycle control, even the best-designed agent logic becomes unpredictable.
2. Reasoning & Intelligence Layer
This layer powers decision-making.
It enables agents to:
- Interpret goals
- Perform multi-step reasoning
- Choose actions intelligently
This is where different types of AI agents emerge – some optimized for planning, others for execution or evaluation. Many AI agent frameworks focus heavily on structuring this layer to keep reasoning consistent and auditable.
3. Knowledge & Context Layer
Agents cannot rely solely on what they “know” from training.
This layer ensures agents:
- Access accurate, up-to-date information
- Ground decisions in trusted data
- Avoid hallucinations in critical workflows
This component is foundational for enterprise-grade AI agent use cases, especially in regulated or data-sensitive environments.
4. Memory & State Management
Memory allows agents to maintain continuity across interactions.
This component handles:
- Short-term task context
- Long-term user or system memory
- State persistence across sessions
Without memory, agents reset on every interaction, which severely limits their usefulness.
5. Tool & Action Interface
Thinking alone isn’t enough. Agents must be able to do things.
This interface allows agents to:
- Interact with APIs
- Query databases
- Trigger workflows
- Execute approved actions
It’s the bridge between intelligence and real-world impact – a key requirement when offering any AI agent development service.
6. Observability, Safety & Governance
As autonomy increases, visibility becomes non-negotiable.
This component provides:
- Execution logs
- Decision traces
- Approval workflows
- Auditability
It ensures that agents remain controllable, explainable, and trustworthy, especially important when evaluating solutions from top AI agent companies.
Why These Components Must Work Together
Each of these elements is interconnected. A powerful reasoning engine without memory leads to inconsistency. Tools without governance create risk. Knowledge without lifecycle management leads to chaos.
Understanding these components at a high level prepares you for the most important question this guide answers next: how to build an AI agent platform step by step without overengineering or creating fragile systems.
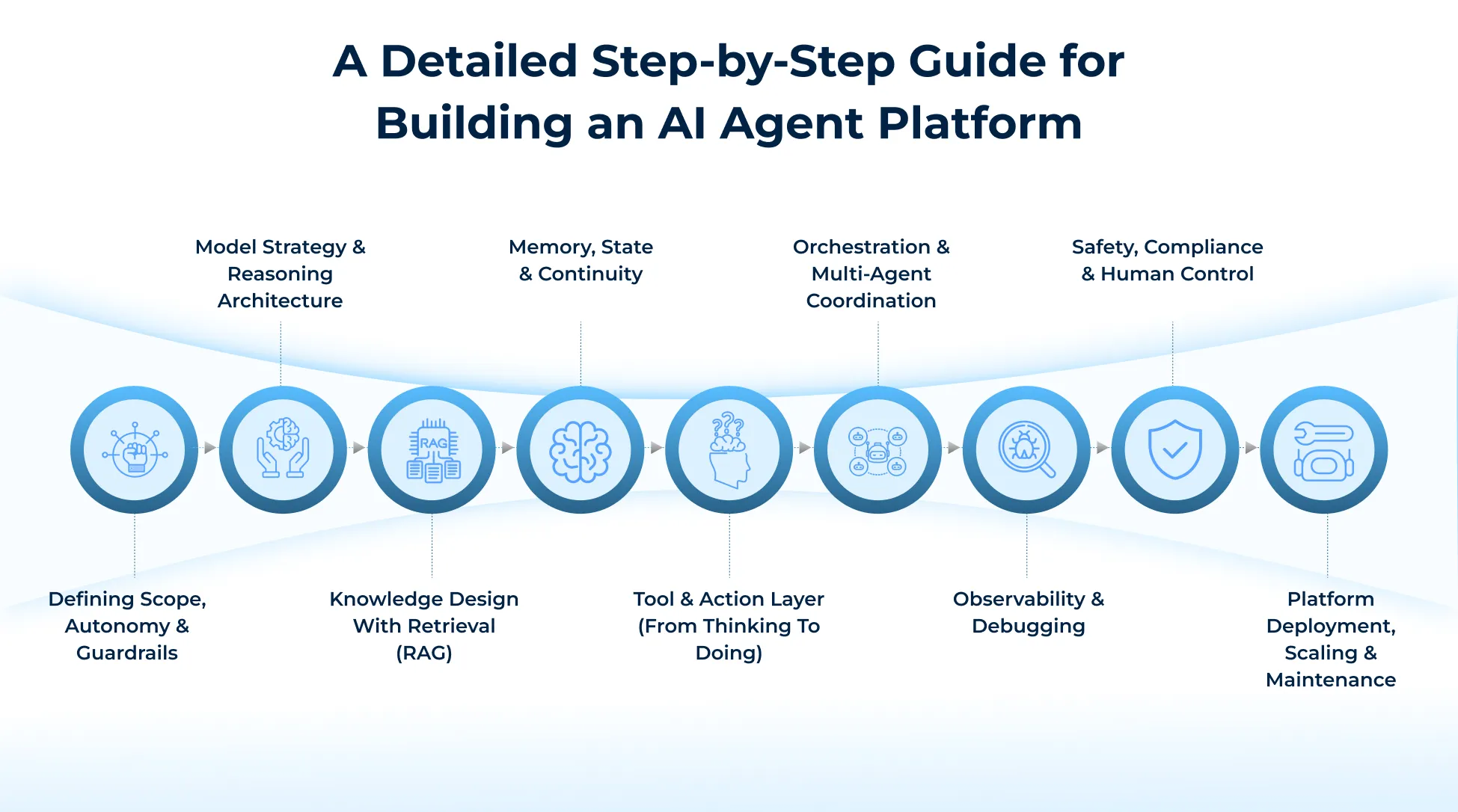
Step 1: Defining Scope, Autonomy & Guardrails
Before writing a single line of code, it’s critical to define scope and autonomy. Most AI agent failures happen not because the technology is lacking, but because agents are given too much freedom without boundaries. A well-defined foundation ensures reliability, safety, and trustworthiness across AI agent use cases.
- Define Core Purpose: Clearly outline the problem the AI agent is solving, the desired outcomes, and what falls outside its responsibility. Specificity prevents misalignment and sets measurable success criteria.
- Determine Level of Autonomy: Decide whether your agent should act in an advisory, assisted, or fully autonomous capacity. Many top AI agent companies start with limited autonomy and gradually increase it, allowing the system to learn and build trust.
- Human-in-the-Loop Oversight: Human supervision is not a limitation—it’s a safeguard. Incorporate approval workflows, real-time intervention, and review mechanisms to ensure unexpected scenarios are handled safely.
- Establish Guardrails: Restrict access to sensitive tools, set execution thresholds, and enforce time or cost limits. Guardrails help agents act intelligently without risking operations or compliance.
This step is foundational when evaluating best examples from top AI agent companies or consulting the most popular AI agent guidebooks. Proper scope and boundaries influence all subsequent design decisions.
Step 2: Model Strategy & Reasoning Architecture
The reasoning architecture determines how your AI agent thinks, plans, and executes. A robust architecture separates reasoning models and execution models to optimize performance across different AI agent use cases.
- Reasoning Models: Handle planning, decision-making, and reflection. They enable multi-step reasoning and autonomous decision loops.
- Execution Models: Focus on structured outputs, tool invocation, and task completion. By separating reasoning from execution, platforms gain reliability, scalability, and easier debugging.
- Hosted vs. Self-Hosted Models: A hybrid approach ensures critical reasoning tasks are fast and reliable while repetitive or high-volume operations remain cost-efficient.
- Reasoning Models: Handle planning, decision-making, and reflection. They enable multi-step reasoning and autonomous decision loops.
- Execution Models: Focus on structured outputs, tool invocation, and task completion. By separating reasoning from execution, platforms gain reliability, scalability, and easier debugging.
- Hosted vs. Self-Hosted Models: A hybrid approach ensures critical reasoning tasks are fast and reliable while repetitive or high-volume operations remain cost-efficient.
- Prompting as Architecture: In modern AI agent frameworks, prompts are structural, guiding agent reasoning instead of acting as one-off instructions. They standardize thought processes and reduce errors.
- Fallbacks and Contingency Planning: Prepare for model timeouts, unexpected outputs, or errors. Robust fallback strategies, such as human escalation or simplified task execution, ensure uninterrupted operation.
This stage ensures your AI agents are not only smart but also consistent, adaptable, and production ready.
Step 3: Knowledge Design with Retrieval (RAG)
Knowledge is the backbone of any AI agent platform. Agents cannot rely solely on model inference – they need access to accurate, verifiable information.
- Knowledge vs. Memory: Knowledge answers, “what is true,” while memory tracks context and past interactions. Both are essential but conflating them can reduce agent accuracy.
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): RAG allows agents to retrieve relevant information before reasoning, ensuring outputs are factually grounded and reducing hallucinations.
- Knowledge Pipeline: Structure your data, preserve metadata (source, timestamp, context), and implement relevance scoring. This ensures agents retrieve precise information quickly, improving reliability across AI agent use cases.
A strong knowledge design improves trust, consistency, and performance in enterprise-grade platforms, a critical consideration for organizations seeking AI agent development services or evaluating solutions from top AI agent companies.
Step 4: Memory, State & Continuity
Memory ensures agents behave intelligently and consistently over time, enabling personalized and context-aware interactions.
- Short-Term Memory: Maintains session context, current goals, and intermediate reasoning steps.
- Long-Term Memory: Tracks preferences, configurations, learned patterns, and historical interactions for continuity.
- State Memory: Preserves workflow progress, allowing agents to resume tasks, avoid duplication, and maintain coherence across complex processes.
Effective memory strategies, such as decay mechanisms and relevance scoring, enhance usability, trust, and overall agent intelligence.
Step 5: Tool & Action Layer (From Thinking to Doing)
Tools are what allow AI agents to act on their reasoning and deliver real-world outcomes.
- Examples of Tools: Internal or external APIs, databases, automation scripts, and workflow triggers.
- Structured Tool Invocation: Agents should interact with tools using clearly defined input/output schemas rather than free-text commands. This reduces errors and ensures predictable behavior.
- Validation & Retries: Platforms must validate actions, retry on failure, and escalate when necessary.
- Permissions & Constraints: Control which agents can access specific tools, tasks, or environments to maintain security and compliance.
This layer transforms intelligence into operational impact, central to high-value AI agent development services.
Step 6: Orchestration & Multi-Agent Coordination
Orchestration enables multiple agents to work collaboratively, maximizing efficiency and reliability.
Coordination Patterns:
- Sequential Coordination: Step-by-step execution, useful for workflows where each step depends on the previous.
- Parallel Coordination: Simultaneous actions for faster results in large-scale tasks.
- Hybrid Coordination: Dynamic combination based on task complexity and priority.
- Communication & Data Sharing: Agents require shared knowledge bases, standardized memory access, and reliable messaging protocols.
- Failure Recovery: Detect errors, retry, escalate, or reassign tasks automatically.
Proper orchestration turns individual agents into a cohesive intelligence network, essential for enterprise AI agent platforms.
Step 7: Observability & Debugging
Transparency and traceability build trust in AI agents.
Key Components:
- Execution Logs & Decision Tracing: Track every agent action and reasoning path.
- Metrics & Alerts: Monitor performance, completion rates, failures, and anomalies.
- Debugging Tools: Inspect, simulate, and replay agent behavior for troubleshooting.
Observability ensures platforms are enterprise-ready, differentiating them from experimental prototypes.
Step 8: Safety, Compliance & Human Control
Safety ensures sustainable, responsible deployment of AI agents.
- Human-in-the-Loop Oversight: Approval gates, real-time intervention, and escalation protocols maintain accountability.
- Compliance: Enforce role-based access, logging, auditing, and regulatory adherence (GDPR, HIPAA, Shariah-compliance).
- Safety Mechanisms: Action filters, rate limits, and sandbox testing prevent harmful operations.
Combining autonomy with oversight delivers reliable, trusted AI agents suitable for mission-critical applications.
Step 9: Platform Deployment, Scaling & Maintenance
Deployment involves more than launching – it requires scaling, monitoring, and continuous improvement.
- Containerization & CI/CD: Use Docker, Kubernetes, and automated pipelines for consistent deployment.
- Horizontal Scaling & Load Balancing: Add agent instances to handle increasing workloads without compromising performance.
- Monitoring & Maintenance: Update reasoning, retrieval, execution models, knowledge, and memory regularly.
- Security & Compliance Maintenance: Continuously enforce access policies, audit trails, and human-in-the-loop controls.
- Continuous Improvement Loop: Collect metrics, debug errors, refine workflows, and expand capabilities for evolving AI agent use cases.
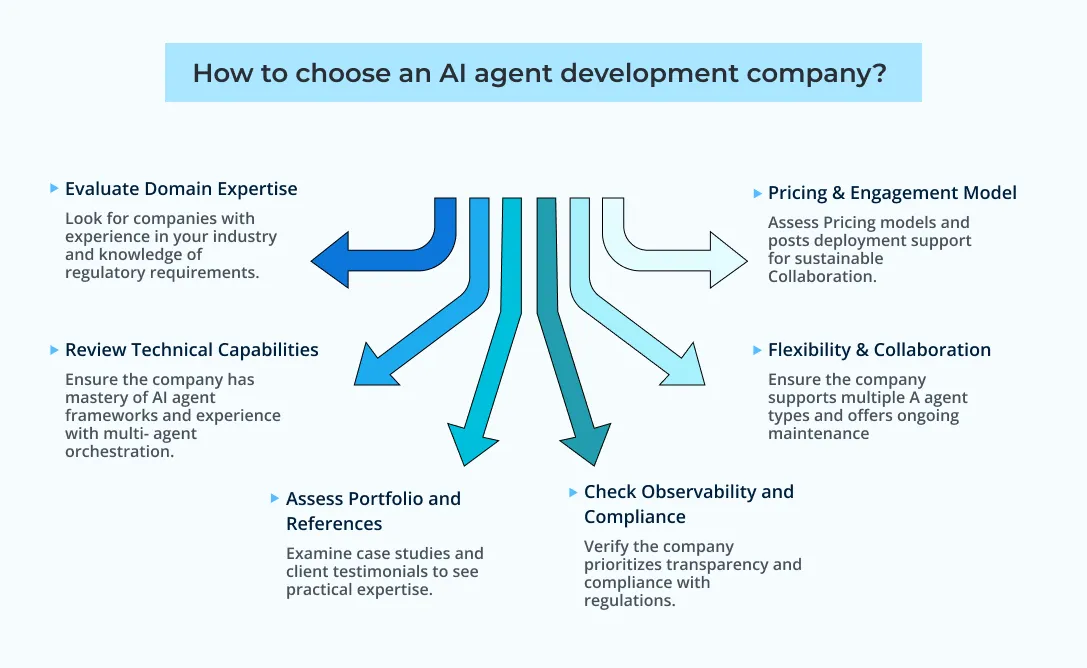
Building an AI agent platform is complex. Many businesses struggle to decide whether to develop in-house or partner with experts. Selecting the right AI agent development service can make the difference between a successful deployment and costly delays.
Here’s a structured approach to choosing the best partner:
1. Evaluate Domain Expertise
Not all AI agent developers are equal. Look for companies with:
- Experience in your industry
- Proven AI agent uses cases similar to your needs
- Knowledge of regulatory requirements and safety standards
Companies with domain expertise can anticipate challenges and deliver platforms faster and more reliably.
2. Review Technical Capabilities
A strong development company should demonstrate:
- Mastery of AI agent frameworks
- Experience with multi-agent orchestration
- Knowledge of RAG, memory, and tool integration
- Ability to design reasoning and decision-making architectures
Technical proficiency ensures your platform will scale safely and efficiently.
3. Assess Portfolio and References
Examine the best examples from the company’s past projects:
- Case studies
- Client testimonials
- Demonstrations of deployed agents
Top-performing companies often showcase projects similar to your requirements, reflecting practical expertise beyond theory.
4. Check for Observability and Compliance
Ensure the company prioritizes:
- Observability & debugging for transparency
- Safety, human-in-the-loop oversight, and risk mitigation
- Compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, Shariah compliance)
This is critical for long-term trust and smooth operation.
5. Flexibility & Collaboration
The ideal partner adapts to your evolving needs:
- Supports multiple types of AI agents
- Offers a modular platform design
- Provides ongoing maintenance and improvement services
Flexibility ensures your platform evolves as new AI agent use cases emerge.
6. Pricing & Engagement Model
Finally, assess the business fit:
- Transparent pricing models
- Clear timelines and milestones
- Post-deployment support
Choosing a partner that aligns financially and operationally with your goals ensures a sustainable, successful collaboration.
Partner with Antier to Launch Your AI Platform!
Crafting Secure, Scalable AI Agent Platforms
Building an AI agent platform is a multi-step journey, from defining scope and autonomy, designing reasoning architectures, and managing knowledge and memory, to orchestrating multiple agents, ensuring safety, and scaling efficiently. Each stage plays a vital role in delivering intelligent, reliable, and trustworthy AI agents and also shapes how to choose an AI agent development company that can successfully bring these components together in a production-ready platform.
When choosing a professional AI agent development service, Antier stands out as a top AI agent company. With proven expertise in deploying multi-agent systems, creating enterprise-grade platforms, and delivering end-to-end solutions, Antier ensures your platform is robust, future-ready, and capable of transforming operations. By partnering with Antier, businesses can develop AI agent platforms that seamlessly combine intelligence, reliability, and scalability – unlocking innovation and delivering measurable real-world results.
Frequently Asked Questions
01. What are AI agents and how do they differ from traditional AI systems?
AI agents are autonomous software entities that can think, plan, and act independently, unlike traditional AI systems that are reactive and only respond to questions or instructions. AI agents can understand goals, reason through multiple steps, and adjust their actions based on outcomes.
02. What benefits are companies experiencing from adopting AI agents?
Companies adopting AI agents report measurable productivity gains, with 66% noting early business value. Additionally, over half of these companies experience outcomes such as cost savings (57%), faster decision-making (55%), and improved customer experience (54%).
03. What is the current state of AI agent adoption in organizations?
While 79% of companies have adopted AI agents in real use, only 35% report broad adoption across workflows, indicating that many organizations are still in the early stages of rollout.







